This architecture is for a major Woodwork Manufacturing organization in Cameroon with an annual turnover of over 150 million Xaf and 40 staff. Her current challenges include but are not limited to: long production times due to lack of proper monitoring and planning systems, delays to generate invoices as they are all done manually, loss of customer and production data, misuse of production materials, and lack of a centralized database.
Thus, the proposal to migrate core operations to AWS Cloud to improve efficiency, automate order and production tracking, secure customer data, digitize invoicing, and implement real-time customer updates not leaving out proper data management and insights.
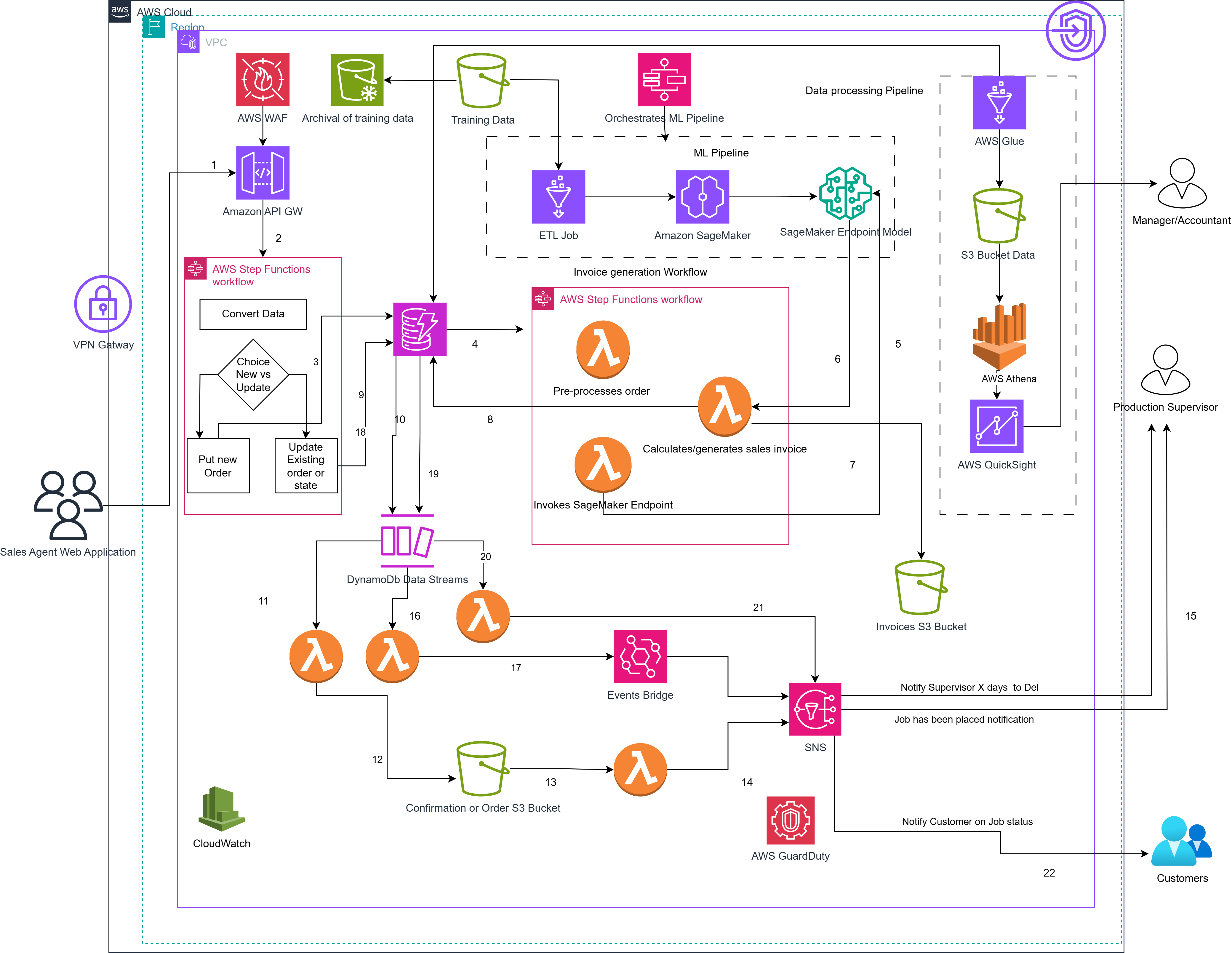
An API Gateway acts as a single-entry point for all client requests, routing them to the appropriate backend services. This is the entry point for external interactions. A Sales Agent initiates an action, placing an order, via an API request.
AWS Lambda is a serverless, event-driven compute service that lets you run code without provisioning or managing servers. Various Lambda functions handle all event-driven compute needs, from initial request processing and real-time DynamoDB stream events, to orchestrating complex invoice generation workflows within Step Functions, and managing confirmations and notifications.
Fully managed NoSQL database offering single-digit millisecond latency. Processed orders and customer data are stored here as the operational database.
Time-ordered sequence of item-level modifications in a DynamoDB table, capturing data changes in near real-time. Captures changes (new orders, updates) and triggers a Lambda function to perform specific tasks.
Object storage for:
Serverless event bus that routes events to targets based on rules. Used to send events to SNS two weeks before expected delivery dates.
Pub/sub messaging service for sending SMS/email messages:
Visually orchestrates distributed applications and serverless workflows. Manages multi-step processes such as:
Cold storage used for:
Uses prepared data from S3 Glacier to train ML models for job duration, cost prediction, and material needs.
Real-time deployment of the trained ML model. Invoked by Lambda to generate predictions used during invoicing.
Serverless ETL for:
Serverless SQL query engine for analyzing S3 data. Utilizes schemas from the Glue Catalog for business reporting.
Business Intelligence service used to create interactive dashboards and visual reports sourced from Athena queries.
Threat detection for monitoring suspicious activity in the account and across services.
Web Application Firewall to protect API Gateway from common attacks such as SQL injection and XSS.
The agent logs in securely (via VPN) and submits a new or updated job request. The request is sent through API Gateway, where AWS WAF filters incoming traffic for threats.
AWS Step Functions receives and inspects the data. It determines whether the order is new or an update and transforms the data into a processable format.
The system writes the job information to DynamoDB. If it’s a modification, the item is updated; if new, it’s inserted. DynamoDB Streams notify other services of the change.
A Lambda triggers Amazon SageMaker to run a real-time prediction from its deployed model. Outputs include job duration, material quantity needed, and minimum pricing with margin (e.g., 35% profit).
Step Functions coordinate a series of Lambda functions that use the prediction result to:
The finished invoice is stored in an S3 bucket. Lifecycle rules archive it to S3 Glacier after a retention period. The linked DynamoDB item is updated to reflect storage status.
SNS sends messages to the production supervisor and the customer. EventBridge schedules future alerts based on expected delivery timelines.
| SN | Pillar | Components | Benefits in Our Architecture |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Operational Excellence |
|
|
| 2 | Security |
|
|
| 3 | Reliability |
|
|
| 4 | Cost Optimization |
|
|
| 5 | Performance Efficiency |
|
|
| 6 | Sustainability |
|
|
Walson Baiye Mboe / AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate / AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner / Student Optima IT (2025)